VOIP
-Introduction
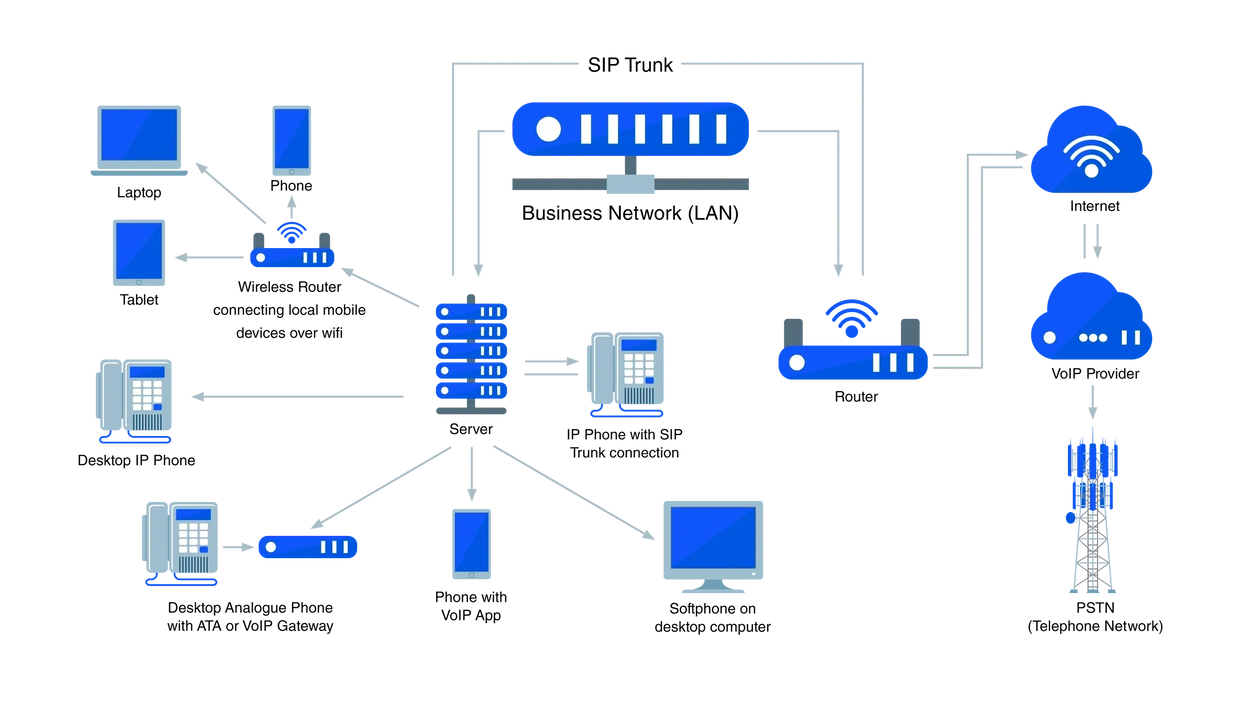
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)
is a type of technology that lets you to make free, or very low cost, calls over the internet.
It doesn’t matter what network or equipment the person you’re calling uses; VoIP lets you call any phone in the world – and you can be reached by any phone. VoIP’s digital nature also allows for new features that were either impossible or very expensive with traditional telephone technology, such as voicemail, call diverts, admin portals, call records, and integration with PCs that allows users to call a number directly from a web browser or address book in an email client.
The intricate, often fragmented nature of business telecom can take some people by surprise. From the sheer variety of the technology in use, to the range of features and functions that are offered by different systems, the thought of adopting an infrastructure that runs on VoIP can be daunting.
In this introduction to VoIP, you will find out all you need to know to demystify the procurement process, ensuring that you can invest in a VoIP solution which is suitable for your business without being deterred by the complexities of the marketplace.
Legacy Solutions
Older telecom technology is based on analogue landline connectivity to the POTS (otherwise known as the Plain Old Telephone Service). This tongue in cheek name is an indication of just how archaic such configurations are considered to be today. And yet in spite of this, plenty of contemporary companies are still reliant upon legacy systems, even if they are eager to migrate to VoIP. The good news is that it is possible to take an incremental approach to upgrading, integrating elements of traditional systems with modern IP-based solutions.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX)
telecom solutions are comprised of on-site hardware which is used to route all calls to and from individual desktop phones through the central connection to the office, otherwise known as the trunk line. The first benefit of a PBX is that employees can make internal calls without having to involve any element of the external network in the process, which reduces the expense of internal communication.
Today, a PBX handles routing automatically. In addition, the bulk of the infrastructure can be hosted off-site, meaning that small businesses can enjoy the benefits of a private PBX in an IP environment without having to make major investments in hardware. By using VoIP, these small businesses will also save on maintenance costs.
The other important acronyms you will need to know to differentiate telecom systems from one another are:
• IP PBX: Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange
• PABX: Private Automatic Branch Exchange
• EPABX: Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange
Why VOIP?
VOIP will reduce your expenses,
* Easy to install and manage.
* Increase in productivity.
* Promotes flexibility.
Our Partners
-









ACTIVE INTEGRATION
22 Mahmoud Hassan, Al Golf, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.

Why Active!
Welcome to Active Integration.
The valuable place for light (low) current systems.
Transforming the idea into a realistic solution, from start to finish, we help get the job done.
Check out our company profile.